In today's article, we're going to talk about the disease of the century - about osteochondrosis (known as rickets in the common man). Previously, the disease was blamed on people over 50, but now it's "younger" and affects everyone, starting with 15-year-olds.
As scary as it may seem, more and more people are being diagnosed with osteochondrosis. According to statistics, nearly 80% of the inhabitants of the earth suffer from this spinal disease.
Read more about the disease of civilization and how to live with it later in this article.
What is osteochondrosis?
This is a bone and cartilage disease that manifests as a degenerative dystrophic disease of the cartilage structure of the spine, causing severe pain.
These degenerative diseases, in other words, changes in the spine occur under the influence of normal life factors, i. e. simply start with the fact that we do something, stand, walk, move, carry heavy objects, etc. Our spine is constantly performing the hardest work, performing three main functions: support, protection (protecting the spinal cord), and devaluation during walking and other body movements caused by the discs.
Gradually, over the course of life, the cartilage wears down and loses moisture, leading to microtears. The height of the disc changes, and the vertebrae begin to irritate the spinal nerves, causing the pain to flare up.
When the disc loses its elasticity, the excess load on it causes what is called a herniation and develops a hernia. It starts to affect the spinal nerves more and in these cases, if we talk about for example cervical spondylosis, the pain radiates to the hands and the fingers feel numb.
If you experience pain in the neck, thoracic spine or lower back, we recommend that you contact a neurologist or chiropractor who specializes in spine-related conditions. The sooner you seek help, the sooner you can get rid of the pain and reduce the risk of complications.
Causes of Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis can develop for a variety of reasons. Experts who study the disease believe that the main reason is that the load on the spine is unevenly and incorrectly distributed. Thus, in places of overload, changes in the disc structure can be observed.
However, there are other reasons for the development of the disease:
- hereditary;
- age-related changes;
- Spinal injury or congenital injury;
- metabolic failure, overweight;
- flatfoot;
- Lazio Campsis;
- concussion;
- various infectious diseases;
- Spinal overload during exercise;
- exposure to chemicals.
There are also so-called risk factors, the presence of which contributes to the development of the disease:
- driving or working in front of a computer every day;
- Intensive, serious training in the gym;
- being overweight;
- unhealthy diet;
- not very active lifestyle;
- smokes;
- low temperature;
- neurological shock;
- incorrect posture;
- uncomfortable shoes and high heels;
- drag weight;
- back muscle weakness;
- Dependent on the weather, living in unsuitable climatic conditions.
If you fall into one of these risk groups, be sure to take osteochondrosis prophylaxis (about a little lower) to prevent osteochondrosis from developing.
Types and symptoms
There are four types of osteochondrosis in total. We will discuss them in this section.
Neck osteochondrosis
It is considered the most dangerous type of disease because the cervical spine is so flexible that even a small load can cause them to move. What is the danger? The fact is that the vertebral artery passes here - it's a blood vessel that affects the pressure and state of the brain. This artery supplies blood to areas of the brain responsible for blood pressure, systolic rhythm, and vestibular stability. When the vertebrae are displaced, the arteries are squeezed, so blood flow is disrupted and the brain no longer receives enough blood. The consequences are headaches, flashing black dots ("flies") in the eyes, dizziness, jump pressure, memory impairment, and general mental decline.
Pain in the back of the neck radiating to the shoulders, under the shoulder blades, arms, fingers becoming numb.
thoracic osteochondrosis
This is a fairly rare condition because the thoracic spine has the least mobility and is well protected by the ribs and muscles. The cause of the development of osteochondrosis in the thoracic region is usually scoliosis (curvature of the spine). It is difficult to identify this particular disease because its symptoms are very similar to other diseases, usually thoracic osteochondrosis causes pain in the area of the heart, which is similar to the symptoms of angina pectoris.
The disorder manifests as spinal pain between the shoulder blades, numbness and weakness of the arm muscles, tingling, pain in the sternocostal area, aggravated by deep breathing.
lumbar osteochondrosis
It is considered the most common type of disease - lumbar osteochondrosis, because the greatest load falls on this particular part of the spine. A sedentary lifestyle has the greatest impact on the lower back. As the nerves in this part of the spine are pinched, a person experiences persistent severe or painful pain in the lower back, usually radiating to the back of the thighs and buttocks, and then to the calves.
Painful attacks are accompanied by numbness, tingling in the toes, and crawling on the back of the leg. The normal function of the genitourinary system and intestines is disrupted.
extensive spinal osteochondrosis
It features the simultaneous defeat of two or all three sections of the ridge.
stage
In this section, we'll discuss how far the disease has progressed, and how they manifest. Modern medicine divides spinal diseases into 4 stages:
- Stage 1
In the first stage, it is quite difficult to diagnose the disease, and in principle, suspect it yourself. Patients experience general back discomfort, which is often attributed to overwork, hard work, stress, or even not wanting to see a doctor. The disease usually progresses slowly and appears in a latent form, usually detected incidentally during a full-body examination (X-ray or MRI) of the patient.
- Stage 2
The second stage is characterized by the onset of pain attacks as the process of cartilage destruction begins. Without treatment, the patient's discs rapidly decrease in size and they slightly protrude, a stage that precedes the formation of a hernia. There is nerve root compression and, in fact, there is a pain syndrome as a result.
- Stage 3
In the third stage, patients experience severe changes in the spine. The development of lordosis, scoliosis, the curvature of the upper part of the spine (kyphosis), the onset of a hump, the appearance of a herniated disc. Of course, proper treatment will no longer fully restore the spine, however, it will appropriately improve its condition and reduce defects such as hump or curvature.
- Stage 4
If the disease has reached stage four, the spine has undergone irreversible changes. Getting around becomes difficult because every movement causes terrible pain. Cartilage is compacted, vertebrae are displaced, and bone tissue grows. Usually at this stage, the patient becomes disabled.
medical treatement
After a specialist (orthopedist, neuropathologist, chiropractor) has made a complete diagnosis and diagnosed osteochondrosis, he prescribes a complex treatment approach, which includes a variety of treatments. With the right combination of them, you can get very good therapeutic results:
- Preparation
First, treatment is aimed at relieving pain attacks, for which analgesics and topical pain relievers are prescribed. Anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, antioxidant treatments are then followed. After that, normal blood circulation needs to be restored.
- exercise therapy
After the drug treatment is over and the inflammation subsides, you can and should go to an exercise therapy class. In principle, you can exercise at home, but it is best to find a specialist to exercise first, and then apply for the knowledge acquired at home.
- manual therapy
Manual therapy is also useful, as it helps increase the distance between the vertebrae, releases compressed nerves and blood vessels, and promotes and accelerates tissue healing. Displaced vertebrae are removed. The main thing to pay attention to when choosing a chiropractor is whether he has a doctor's diploma, a neurologist certificate, or a chiropractor certificate. If at least something is missing, then you should not be treated by this specialist.
- acupuncture
Reflexology (acupuncture) is also effective. It can be said that it has a miraculous effect, almost from the first session you will feel its analgesic effect, the swelling of the area where the nerve is pressed will subside, and the muscle spasm caused by the pain attack will also be relieved. Reduces inflammation, eliminates numbness in the fingers, characteristic of this disease, restores the passage of nerve signals.
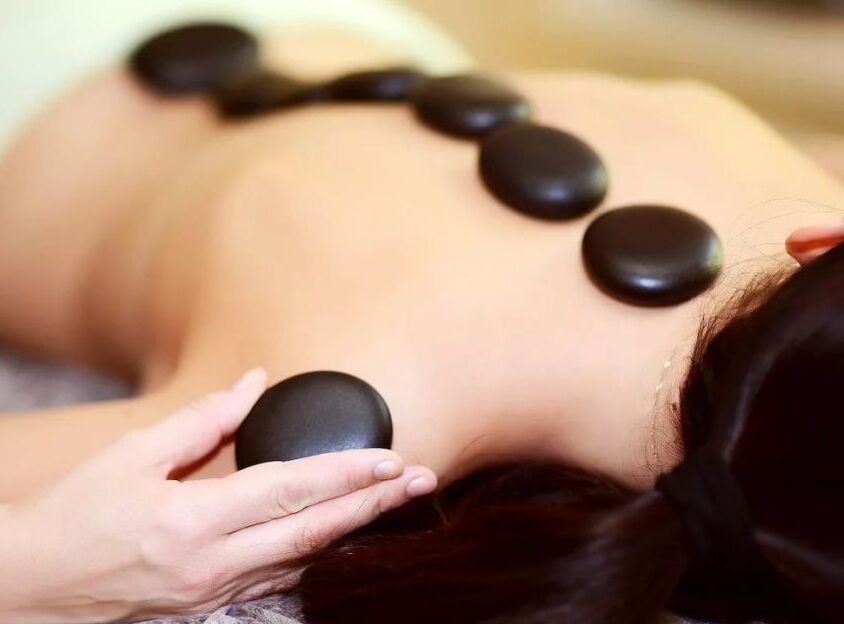
- stone therapy
Stone therapy or stone therapy works well to heat the muscles and improve blood flow and nutrition to the discs.
- Magnetic therapy
With magnetic therapy, the patient will also feel better. It helps reduce blood viscosity, improve nutrition of damaged tissue, reduce swelling, restore mobility and more.
- swimming pool
Many times, the patient is advised to do special exercises in the swimming pool as well as to float - this process allows you to completely relax the spine due to being in the salt solution, so the patient "floats" and all the load is taken from the spine.
In principle, as a preventive measure against osteochondrosis, you can go to any SPA salon to float, and this service is offered almost everywhere.
- Operation
In extremely severe cases, surgery is performed during which the hernia and affected disc are removed and the spinal structure is stabilized. Surgery is a big risk to the patient, so it is performed in an emergency.

In the early stages of osteochondrosis, you can get rid of it quickly, all you need is some exercise to prevent it from developing again. Integrative therapy will be selected by the attending physician based on all the characteristics of your body.
treatment at home
As we mentioned above, it is important to perform the first exercise of exercise therapy under the supervision of an expert so as not to overload the spine. But after a few lessons, you can practice at home.
After home gymnastics, it is recommended that people diagnosed with spinal diseases do self-massage, and you can ask people around you to help.
You need to start with gentle strokes along the entire spine. Then knead the muscles of your neck, chest, and lower back in circular or pinching motions, without having to press hard with your fingertips. You can also rub the spaces between the ribs without pressing too hard.
Eating right is very important if you suffer from the diseases we discuss in this article. Which diets to follow and which foods are best to exclude from the diet in the next section.
osteochondrosis diet
Proper nutrition for osteomalacia includes the use of products containing substances that promote cartilage formation in the spine - mucopolysaccharides. Most of them are all kinds of jellies, jellies, fish jelly. For desserts, jelly is perfect, where the main ingredient is gelatin, which in turn is rich in mucopolysaccharides.
Also, you need to drink plenty of water, and lack of water can lead to disc damage that can lead to the first manifestations of the disease.
Vegetables and fruits are one of the most important foods for rickets, and their use is necessary for the healthy functioning of the spine. They contain polyunsaturated fatty acids needed by the human body.
What can and should you eat?
The body needs many trace elements:
- One of them is calcium, which is found in milk, almonds, hard cheeses, cottage cheese, beans.
- Vitamin D is necessary for the absorption of calcium: eggs, fish, butter. Also, regular sun exposure is recommended.
- Calcium is only stored in bone tissue along with adequate amounts of magnesium in the body; it is found in cucumbers, nuts and avocados.
- Also, it is important to eat foods that contain phosphorus: fish, soybeans, peas, cabbage.
- B vitamins are also important to our disease, to get them you need to eat: beef, pork, mushrooms, seafood, grains. Vitamin A is also useful and is found in carrots, melons, squash, and liver.
In general, as you can see, the diet isn't terrible, you don't have to go hungry, you just have to exclude things from your menu, but there are things that can replace these products.
what is not recommended
- The first thing to say is to reduce your salt intake. Especially if you have cervical osteochondrosis, a salt-free diet can be useful.
- The ban also includes marinades, semi-finished products, spicy food, and pickles.
- Sweets, like salt, slow down blood circulation and will only make things worse if the blood supply to our brain is already disrupted.
- We left coffee and various sodas off the menu because they are good at flushing out calcium from the body, as well as potassium, magnesium, and other important minerals.
And, of course, monitoring your weight is very important, especially with lumbar spondylosis, since all the major loads are already taken on by the lower back, imagine how difficult it would be for him to cope if the weight is heavy!
Diet can also act as a preventive measure, and even if you do not have a diagnosis of osteochondrosis, all the vitamins and minerals shown in the osteochondrosis diet are very useful to your body in any situation.
Listen carefully to your body and don't be afraid to seek help from your doctor if necessary.
We wish you good health!