Causes of lumbar osteochondrosis
- Genetic predisposition to diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- smokes;
- previous injury;
- hormonal and vascular diseases;
- Being overweight;
- The muscles are too weak to provide necessary support to the spine;
- Professional activities related to heavy manual labor (athletes, loaders).
Development stages of lumbar osteochondrosis
- The first stage (degree) is characterized by mild symptoms. The sensation of pain is generated against the background of stimulation of nerve endings by the nucleus pulposus and penetrates into the cracks in the annulus fibrosus.
- The second stage is characterized by displacement of the upper vertebrae relative to the lower vertebrae due to breakdown of the core and annulus. These pathological processes can lead to neurological symptoms, numbness and instability in the affected area, in addition to pain during movement.
- The third stage is characterized by increased pain and disc herniation due to disruption of the integrity of the annulus fibrosus. Pain, sensory disturbances, and muscle weakness can interfere with daily tasks. Due to nerve root compression, the function of the urinary and intestinal systems may be disrupted.
- The fourth stage corresponds to the complete destruction of the intervertebral discs, they become fibrotic, and osteochondral growth of the vertebral bodies leads to immobility of the spine in this part.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
- Neurologist
- Orthopedist
- therapist
- In the early stages, when degenerative changes are just beginning to appear, symptoms are mild.
- The intermediate stage is characterized by weakening of the annulus fibrosus, which may already manifest as low back pain.
- Later, when the structures become fibrotic and osteophytes form, the pain becomes less noticeable, but the mobility of the spine is significantly reduced.
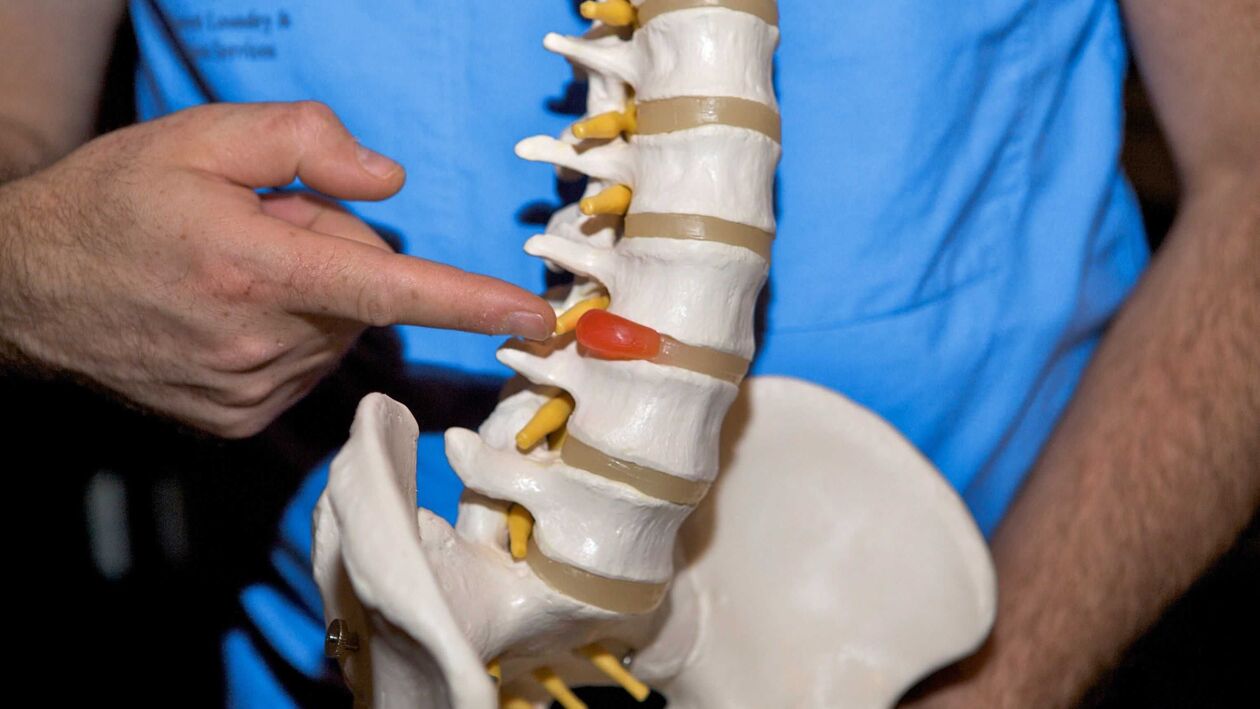
Diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis

- An MRI shows hydration (water saturation), the shape of the disc, and its height, allowing the identification of compressed nerves.
- CT scans allow you to study tissue conditions in detail and diagnose disease at an early stage.
- Provocative discography to determine the location of the affected disc.
Treatment methods for lumbar osteochondrosis
- Daily living, including adequate rest and adequate physical activity;
- Perform regular physical exercise to enhance muscle strength;
- Lifestyle modifications, including nutrition review and weight loss.
physiotherapy

- Electrical stimulation. Electrical pulses help relieve back pain and improve blood circulation to the affected spine.
- Ultrasound therapy. Ultrasound can penetrate deep into tissue and help relieve inflammation and pain.
- Magnet therapy. Magnetic fields can improve blood circulation and metabolic processes in tissues and promote their regeneration.
- Laser Treatment. Laser beams can help relieve pain, stimulate blood circulation, and stimulate tissue regeneration.
- Ultrasonic electrophoresis. This method combines ultrasound therapy with the use of medications, which can penetrate deep into tissue and help relieve inflammation and pain.
medical treatement
Surgery
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis at home
- Applying heat to the lower back can improve blood circulation and relieve muscle spasms and tension.
- Ice packs can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Massage can also relieve pain by relaxing muscles, relieving spasms, and reducing pressure on the spine. By increasing blood circulation to the area, metabolic processes are improved and the tissues are enriched with oxygen.
- Use orthopedic mattresses and pillows. They will help maintain the correct position of the spine during sleep.
- Proper distribution of load on the spine. When lifting heavy objects, you should use correct lifting techniques to avoid pressure on the lumbar spine.
- Proper nutrition. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamins helps keep bones and joints healthy.
Which doctor should I contact for lumbar osteochondrosis?
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
Prevention of lumbar osteochondrosis
- Get regular physical activity. Stay in good physical condition. Strengthen back muscles. Back stretching and strengthening exercises will help keep your spine healthy.
- Reduce Spine Stress: Avoid unnecessary stress on your spine. When lifting heavy objects, use proper lifting techniques.
- Posture Correction: Ensure correct posture. Sit up straight, stand up straight, don't slouch. Choose an orthopedic pillow and mattress for sleep to maintain the correct position of your spine while you rest. Invest in quality shoes with good cushioning and support.
- If due to the nature of your profession you are forced to sit for long periods of time, use an orthopedic chair to protect your back. Avoid staying in one position for long periods of time. Take regular breaks and stretch your spine.
- Watch your weight. Being overweight can put extra stress on your spine.
- Avoid uncontrolled movements and back injuries. Use caution when engaging in sports or physical activity.
- Quit smoking, which can have a negative impact on your spinal health.